Content
- 1 External SSD vs Internal SSD
- 2 SSD Interface
- 3 What is an Internal SSD?
- 4 Internal SSDs form factors
- 5 Advantages of an Internal SSD
- 6 What Is An External SSD?
- 7 External SSD form factor
- 8 Advantages of an External SSD
- 9 What is the difference between Internal and External SSD?
- 10 Is it better to have internal SSD or external SSD?
- 11 Can I use external SSD instead of internal SSD?
External SSD vs Internal SSD
The world of SSD has been flourishing over the past decade because of its ability to deliver more data at faster speeds than traditional hard drives. However, there’s a lot more than just solid-state drive (SSD) and hard-disk storage drive (HDD) that you should be aware of if you’re building a new computer or looking to replace the storage media in your current one.
There are many different types of SSDs on the market, and each one has its own set of strengths and weaknesses. If you’re looking to maximize your storage capacity or want to make sure that your computer is as fast as possible, there’s a lot more than just size that you need to consider when shopping for an SSD.
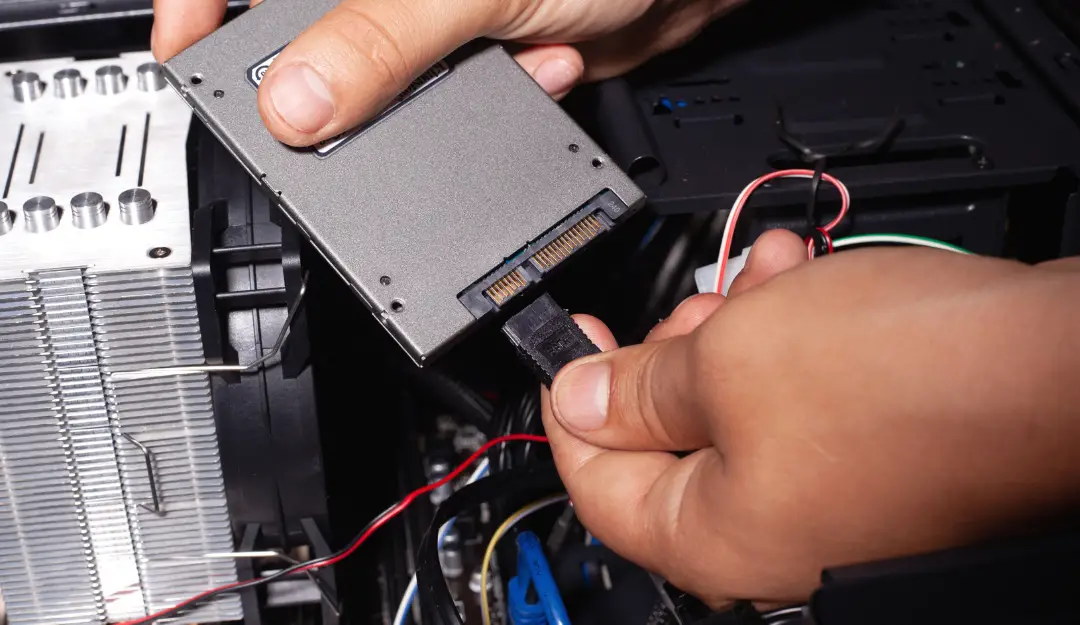
Internal solid-state drive and external solid-state drive are the two types of solid-state drives that exist in the market. The former is integrated into a computer while the latter is connected to the motherboard via USB or any port.
In this article, we’ll show you the differences between an external SSD and an internal SSD, so that you can make an informed decision when it comes to purchasing one of these drives.
SSD Interface
Solid state drives (SSDs), like traditional hard drives, are used to store data. However, unlike a hard drive which consists of moving parts and has a spinning disk, an SSD has no moving parts. This means that SSDs are less susceptible to damage from drops or shocks.
The classification of SSDs is based on the type of interface used. Typically, there are two types of interfaces: SATA (Serial Advanced Technology Attachment) and PCI-Express (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express).
PCI-Express is a serial bus architecture developed by Intel Corporation. It plugs into a socket on the motherboard and has a maximum speed of 985 MB/sec. A PCI-Express SSD can be either an internal or external drive, depending on where it’s placed in your computer. Most PC manufacturers use external PCI-Express SSDs to replace hard drives in laptops and workstations for data storage and backup purposes.
SATA (Serial Advanced Technology Attachment) is an interface standard for connecting storage devices such as hard disks, optical drives, and solid state drives (SSDs) to host controllers in computers. It is also used for connecting modems with ISDN adapters to telephone lines, and other peripherals to computers or embedded systems using serial ATA (SATA) cables or fiber-optic cables.

What is an Internal SSD?
An internal SSD is a solid-state drive that is installed inside of a computer. Internal SSDs are often used in laptops and smaller devices because they’re not as easy to swap out as external drives. They can also be used in desktop computers, although this isn’t common because it’s expensive to upgrade a desktop computer’s hard drive with an internal SSD.
The main benefit of an internal SSD is that it provides faster performance than traditional hard drives. This is because there are no moving parts in the drive, so there’s no lag while the disk head travels back and forth across the platter. Internal SSDs having no moving parts makes them ideal to withstand more physical shock than regular hard drives, which makes them ideal for notebooks or other mobile devices that might be dropped or jostled around frequently.

Internal SSDs come in various sizes and capacities, but most fit into standard 3.5-inch bays found on desktop PCs. Some higher-end models may require an additional slot on the motherboard, but most will work without any special configuration
Internal SSDs form factors
Internal SSDs are the most common type of solid-state drive. They typically come in three form factors: 2.5-inch, M.2, and mSATA.
2.5-inch Internal SSDs
The 2.5-inch internal SSD is the most common form factor for consumer applications and has been around for a long time. It comes in many different sizes, from 80GB to 1TB or more, and can connect to your computer’s motherboard via a SATA cable or an interface that runs over the mSATA interface (which is smaller than a regular SATA cable).
M.2 Internal SSDs
M.2 drives are newer than 2.5-inch drives and are commonly used in newer laptops and desktops with thinner designs or smaller cases where there isn’t enough room for a traditional 2.5-inch hard drive bay or slot on the motherboard itself (although some laptops still use 2.5-inch bays). The M version of this form factor was designed specifically for laptops, but it can also be used in desktops if they have a spare PCIe slot available (which most do nowadays).
mSATA
mSATA is the smallest form factor for solid state drives (SSDs). It’s used in laptops and embedded systems. mSATA stands for mini-SATA, which is a small SATA connector. The Mini-SATA Connector specification was approved by the Serial ATA International Organization in December 2009. The mSATA standard supports data transfer speeds up to SATA Revision 3 (6Gbps) using the PCI Express Mini Card physical layer specification. It can also be used with SATA II (3Gbps) and SATA I (1.5Gbps).
Advantages of an Internal SSD
Speed
Internal SSDs are faster than hard drives for a variety of reasons. One reason is the absence of moving parts and the other is the ability to read and write data in parallel. A hard drive must read or write data one bit at a time, whereas an SSD can do both simultaneously. This means that if you have 10GB of data to read from the hard drive, it will take twice as much time as reading 5GB would — because the first 5GB can be read while the second 5GB is being written. With an internal SSD, all 10GB can be read at once, saving time and preventing wear on your computer’s components.
Saves Time
An internal SSD also saves time by speeding up boot times and system responsiveness. You’ll notice that your computer boots within seconds after you turn it on instead of waiting for minutes or even hours as with a mechanical hard drive (HDD). This makes it easier for you to use your computer without having to wait for long periods of time before every action you perform.
What Is An External SSD?
An external SSD drive is a portable storage device designed to be used in conjunction with a desktop or laptop computer. The primary benefit of an external SSD is its small size and lightweight, which makes it easy to carry around.
The first thing you’ll notice about an external SSD is that it has a larger capacity than standard USB flash drives. This means that you can store more data on it than on a flash drive, but also that it will take up more room on your desk or in your bag.
In addition to the increased capacity, an external SSD has much faster read/write speeds than standard USB flash drives. This makes them ideal for storing large amounts of data or for transferring large files between computers quickly.

External SSD form factor
External SSD
Portable solid-state drives, such as Crucial’s X8 and X6 products, can be used in place of traditional hard drives. Portable SSDs use the same technology found in 2.5-inch, mSATA, and M.2 devices with an added case and cable interface to increase storage capacity for nearly any computer, tablet, phone, or game console. The X8 works with Windows, Mac OS X 10.6 or later, iPad Pro, Chromebook™ 11 and higher, Android™ 4.4 or later (KitKat), Linux kernel 2.6 or later and Microsoft Windows Embedded Compact 7/8/8.1/10 and is backward compatible with USB 3.0/2.0 interfaces that support UASP for even faster data access speeds up to 450 MB/s read and 440 MB/s write speed performance
Advantages of an External SSD
Portability
One of the biggest advantages of using an external SSD is its portability. External SSDs are designed to be ultra-small and lightweight, so you can easily carry them in your backpack or laptop bag. This makes them ideal for use with laptops, which often lack enough internal space to accommodate large storage drives.
If you’re a road warrior who travels frequently, you’ll appreciate how easy it is to take your external SSD along with you on business trips and vacations. You can safely store all of your important files on your external SSD and take them with you wherever you go.
Ease of Use
Another advantage of using an external SSD is its ease of use. An internal hard drive requires special tools and software to install it properly in your computer. You need to connect the drive through a SATA or USB cable, open up your PC’s case, locate an available slot inside the computer where the drive can be installed (usually under the motherboard), attach a power source and then secure everything in place by tightening screws. Then there’s installing software drivers for Windows or macOS so that your computer will recognize the drive when it’s connected via USB or SATA. With an external SSD, there’s no need for any of this
What is the difference between Internal and External SSD?
Speed
Internal SSDs are faster than external ones because they have fewer components and shorter cables.
The storage capacity of an internal SSD is limited by the size of the computer’s internal bay and the drive’s physical dimensions. The more expensive M2 (or “gum stick”) form factor has a smaller footprint than M.2, but it still has a maximum capacity of 1TB.
External SSDs are typically sold in larger capacities (up to 6TB), but you can only install them in external enclosures that connect via USB or Thunderbolt 3. Because they use USB or Thunderbolt 3, they don’t offer as much bandwidth as PCIe-based internal drives; they’re also slower because they have more components (including a separate power supply).
Portability
Internal SSDs are installed directly onto your computer’s motherboard. This can be done by removing the original hard drive and replacing it with the internal SSD, or by installing an add-in card that allows you to replace your current hard drive or SDD with an internal SSD.
External SSDs are designed to be connected to a computer through a USB port or other type of port.
The main advantages of an external SSD are its portability and its ability to be used as a backup device. You can use an external SSD to store your most important files and documents on it, then take it with you wherever you go so that you don’t need to worry about losing anything important in case something happens to your main computer while away from home or office.
Price
Internal SSDs can be more expensive because they require an adapter to fit into a laptop or desktop computer, while an external drive can be purchased without an additional part. A good comparison would be comparing the price of an internal hard drive with an external one. Internal hard drives have the added expense of an adapter, whereas external hard drives don’t need one.
External SSDs are typically cheaper than internal ones because they don’t require additional parts like adapters or cabling to function properly. However, some external models come with their own power supply, which can make them more expensive than internal models with adapters but no power supply (which usually come from your computer itself).
Is it better to have internal SSD or external SSD?
There is no universal answer as to which storage option is better. It depends on the use cases and requirements. For instance, if you want to store your data securely while using it on multiple devices, an external SSD is a more viable option. On the other hand, if you want to do away with the hassles of wires and cables, speed up your computer, and don’t mind paying more, an internal SSD is preferable.
FAQ,s
Can I use external SSD instead of internal SSD?
Yes, you can use an external SSD instead of an internal SSD. The main difference is that you have to connect the external SSD via USB, and therefore it will not be as fast as an internal SSD because it’s not directly connected to your motherboard.






